Unveiling hidden insights with thermal data
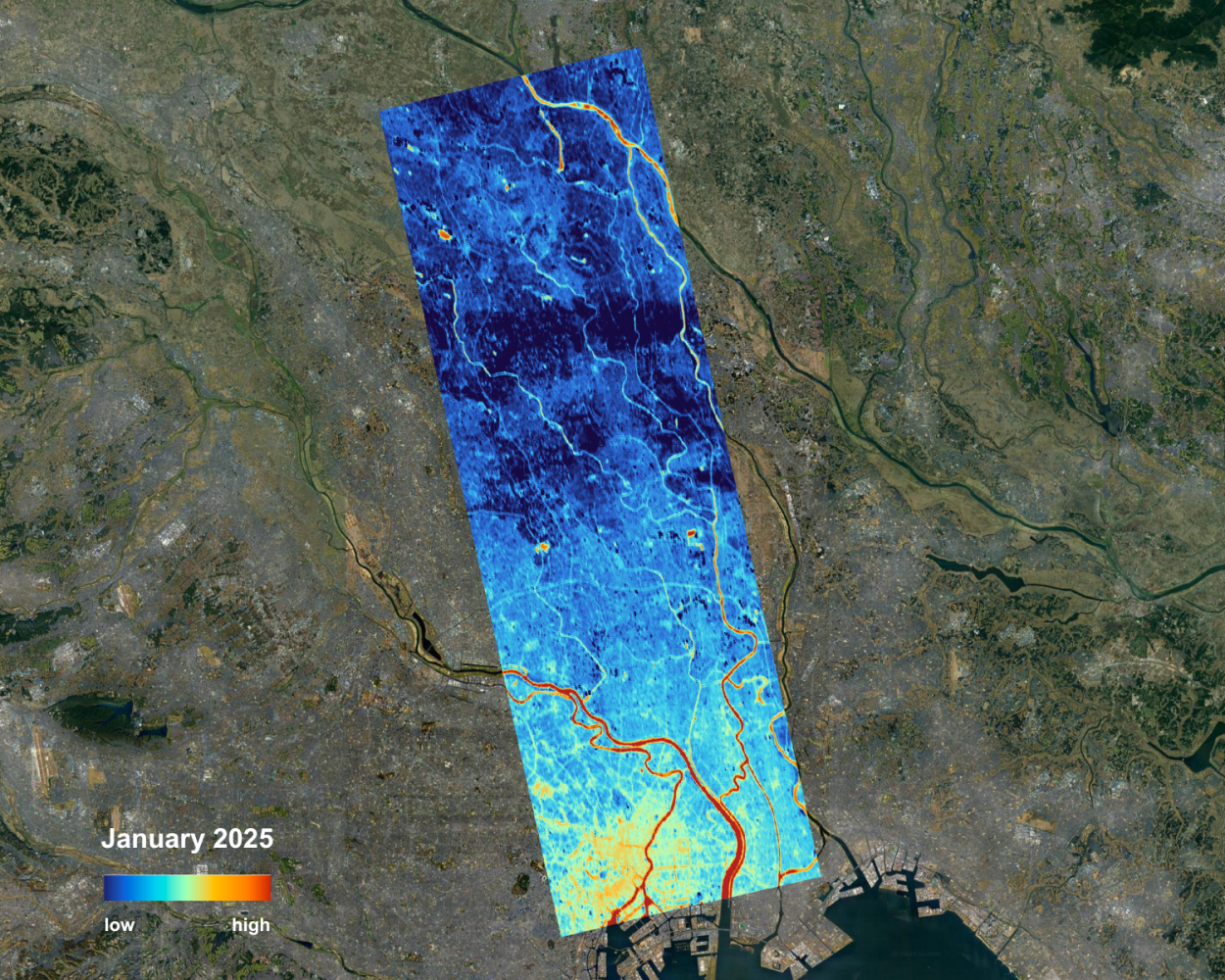
Thermal satellite imagery provides a direct window into Earth’s temperature patterns by detecting the heat emitted from the surface, offering insights invisible to conventional optical sensors by providing land surface temperature (LST). Surface temperature is a fundamental driver of ecosystem processes, infrastructure behavior, and climate-related change. By mapping heat distribution and tracking temperature dynamics, thermal data plays a crucial role in understanding ecosystem functioning, monitoring infrastructure performance, and detecting the impacts of climate variability and change.
Beyond environmental monitoring, thermal observations support applications in disaster response, border monitoring, vessel monitoring, and situational awareness by revealing thermal anomalies associated with wildfires, energy infrastructure disruptions, or unusual heat signatures in remote areas on land and sea. These capabilities contribute to resilience planning and operational awareness while providing a layer of insight that complements conventional imagery for organizations focused on humanitarian, security, and critical infrastructure protection missions.
Surface temperature measurements play a vital role in advancing progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Adopted in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, the SDGs form a global blueprint for peace, prosperity, and environmental stewardship. Temperature monitoring plays a critical role in achieving at least 14 of the 17 goals.

LST reveals processes invisible to optical imager, such as evapotranspiration in crops, surface and urban heat islands, or anomalies in industrial infrastructure. Together, optical and thermal data create a richer, more actionable picture of our planet’s surface dynamics.
There are many advantages of thermal data, find below a few of the most important ones:
- Faster insights: Temperature is a physical variable, which is a lot closer to insights in many use cases compared to visual data (and will hence need less computational effort to extract the same insights). While there are many reasons why leaf colour changes, temperature-derived vegetative stress is a direct quantification of the health of a plant, on which one can act. Road temperatures directly link to road erosion and maintenance requirements, the heat radiation from a building is highly related to its material and insulation.
- Early warning capabilities: Anomalies in temperatures, be it in ways of detecting vegetative stress, the radiative heat of a power plant, or monitoring pollution in rivers, indicate symptoms of early damage, even before it is visible to the eye. A loss of yield, a power outage, or an algae blooming downriver can be better prepared for with an earlier understanding of risk and providing the capabilities of early warnings.
- Predictive: By using physical and AI models that fill gaps between thermal data points over time and space, we can project these insights into the future. This effectively enables forward-looking analysis to anticipate upcoming thermal conditions, enabling proactive decision-making for operations, maintenance, and network planning.
Today, thermal Earth observation (EO) data holds immense strategic value, constellr is a key player delivering high quality, spatial resolution, and precision LST. constellr’s LST is improving global and temporal coverage of thermal data, to deliver new value across cities, farms, and ecosystems worldwide.
For more information on the different products offered by constellr, see the Portfolio

Your gateway to decoding Earth's temperature.
From pixels to planetary resilience.
Explore constellr's data, learn about thermal intelligence, explore our use cases and download actionable demo data sets.